Обоснование
Атопический дерматит (АтД) является одним из наиболее распространенных хронических воспалительных заболеваний кожи. При манифестации преимущественно в детском возрасте распространенность АтД среди взрослого населения может достигать 8%, при этом отмечается глобальная тенденция к росту данного показателя во всех возрастных группах [1, 2]. Согласно многонациональным исследованиям, не менее трети взрослых больных страдают от среднетяжелого или тяжелого АтД [3].
Болезнь демонстрирует высокую гетерогенность в своем течении, а индивидуальные вариации труднопрогнозируемы [4]. Клиническая картина характеризуется чувствительной к внешним факторам ксеротичной кожей, локальными или диссеминированными полиморфными экзематозными высыпаниями, в большинстве случаев сопровождающимися интенсивным зудом [5]. Особенности клинического фенотипа зависят от возраста пациента, продолжительности и степени тяжести болезни, наличия мутаций в генах белков «рогового конверта», типа АтД и этнического происхождения больного [4, 6].
Помимо физических проявлений наличие АтД негативно сказывается на качестве жизни больных и их близких, способствуя нарушению сна, снижению работоспособности и психическим расстройствам [4, 7]. При этом интенсивность дезадаптирующего влияния во многом зависит от тяжести заболевания [8].
Этиопатогенез АтД представляет собой взаимодействие генетических и экспосомальных факторов, что приводит к нарушениям иммунной регуляции и барьерной функции кожи [9]. Присущие болезни цитокиновые аберрации обнаруживаются в пораженной коже, а при тяжелых формах болезни и на неизмененных участках указывают на системность процесса [10]. Доминирующая роль цитокинов 2-го типа в этих патологических изменениях общепризнанна и подтверждается высокой экспрессией интерлейкинов (ИЛ) ИЛ-4 и -13 у всех пациентов [11]. Однако вариабельное участие T-хелперов (Th) типа 1, Th17 и Th22, обусловливающее неоднородность фенотипов АтД, отражает иммунологическую сложность болезни [1, 11].
Высокая распространенность тяжелых форм, хроническое течение и негативное влияние болезни на жизнь людей налагают высокие требования к эффективности и безопасности терапии [12]. Топические средства являются базовым и безопасным способом контроля заболевания, но им присущ ряд недостатков: они не воздействуют на системное воспаление, ограниченно профилактируют обострения, а также малоэффективны при заболеваниях среднетяжелого и тяжелого течения [5]. В то время как традиционные системные препараты глюкортикостероиды и циклоспорин способны помочь при рефрактерных формах АтД, их долгосрочное использование ограничено как часто возникающими побочными эффектами, так и профилями безопасности [5, 6]. Актуальность проблемы неудовлетворенности в результатах терапии распространенных форм АтД подтверждается активно расширяющимся арсеналом системных лекарственных средств [13].
Несмотря на доминирующую роль Th2-ответа, направленные воздействия на ИЛ-4 и -13, оказались менее эффективны, нежели таргетный подход при псориазе. Это несоответствие может быть связано с мульцитокиновой активацией при АтД в отличие от Th17-центрированной сигнализации при псориазе [14]. В этом контексте ингибирование членов семейства янус-киназ (JAK), опосредующих широкий спектр цитокиновой сигнализации, выглядит высокоперспективным [1, 15]. В данном клиническом случае представлен успешный пример применения перорального JAK-ингибитора упадацитиниба взрослым пациентом с тяжелым течением АтД.
Клинический случай
Пациент Г. 29 лет наблюдается в отделении дерматовенерологии и косметологии Поликлиники № 1 УДП РФ с диагнозом АтД. Болен с детского возраста, с 25 лет заболевание приобрело непрерывно рецидивирующее течение с редкими периодами частичной ремиссии. Расположение высыпаний на открытых участках тела и выраженный зуд кожных покровов обусловливали значительное влияние болезни на жизнь пациента. При терапии заболевания применялись эмоленты, топические глюкокортикостероиды, инъекционные формы антигистаминных препаратов, короткие курсы системных глюкокортикостероидов без значительного влияния на течение процесса.
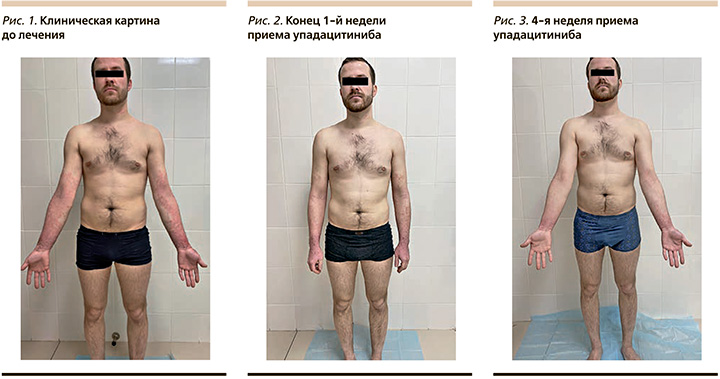
Состояние пациента до начала применения упадацитиниба: патологический кожный процесс хронического воспалительного характера, распространенный, симметричный. Локализуется на коже лица, шеи, верхних и нижних конечностей. Представлен на коже лица диффузно распределенными розовато-красноватыми пятнами, склонными к слиянию, с наибольшой интенсивностью окраски и инфильтрации в периорбитальных областях, пятна с нечеткими границами, слабовыраженным мукоидным шелушением, несколько лихенифицированы, в периорбитальных областях отмечается усиленная складчатость кожи, на кожных покровах шеи и подколенных ямок располагаются единичные разрозненные бледно-эритематозные пятна неправильных округлых очертаний, несколько лихенифицированные и экскориированные, с нечеткими границами и незначительным по интенсивности мукоидным шелушением.
На верхних конечностях процесс представлен сливающимися эритематозными пятнами, вовлекающими практически универсально кожные покровы кистей, предплечий и дистальных третей плеч, пятна с выраженными явлениями лихенификации, нечеткими границами, обильным мукоидным и мелкопластичнатым шелушением, мокнутием, множественными экскориациями и серозно-геморрагическими корками в пределах предплечий и кистей. SCORAD 70 DQLI 20.
На основании тяжести течения АтД, рефрактерности заболевания к проводимому лечению и значительного влияния на качество жизни пациенту назначен ингибитор JAK1 упадацитиниб в дозе 15 мг/сут. Уже к концу 1-й недели лечения пациент отметил значительное уменьшение интенсивности зуда и его влияния на качество сна. Клиническая картина также претерпела изменения в виде ликвидации явлений мокнутия, уменьшения интенсивности окраски и шелушения высыпаний. Эти изменения также были отмечены в показателях SCORAD и DQLI. К концу 4-й недели приема упадацитиниба пациент указывал лишь на редкие низкоинтенсивные эпизоды зуда, нормализацию качества сна. Площадь вовлеченной кожи значительно сократилась, как и выраженность клинических проявлений.
Результаты
Результаты представлены на рис. 1–3. До лечения показатели SCORAD составляли 70, в конце 1-й недели терапии – 52, к концу 4-й недели – 19. До лечения значения DLQI составляли 20 баллов, что отражает очень сильное влияние кожного заболевания на повседневную деятельность пациента, после 1-й недели терапии – 11, после 4 недель – 2 балла. Таким образом, весьма ограниченная продолжительность применения упадацитиниба способствовала минимизации влияния АтД на жизнь больного, несмотря на предшествовавшие тяжесть и рефрактерность заболевания к терапии.
Отмечается хорошая переносимость препарата, из заявленных побочных эффектов у пациента имелись кратковременные симптомы острого респираторного заболевания на 3-й неделе применения джакиниба, не потребовавшие изменений в тактике лечения.
Обсуждение
Семейство JAK состоит из 4 членов и опосредует эффекты более 50 цитокинов и факторов роста, являясь важным участником широкого спектра физиологических и патологических процессов организма [16]. Упадацитиниб – это обратимый ингибитор JAK 2-го поколения, который проявляет селективность в отношении субтипа JAK1 со значительно меньшим влиянием на JAK2, JAK3 и тирозинкиназу 2 [17]. Такой избирательный подход позволяет оказывать полицитокиновое воздействие и уменьшать интенсивность эффектов Th1-, Th2-, Th17- и Th22-сигнализации, сведя к минимуму негативное влияние лекарственного средства на физиологические процессы [7].
Эффективность препарата подтверждена в двух крупных рандоминизированных клинических исследованиях (РКИ) III фазы Measure Up 1 и Measure Up 2. Так, через 16 недель от 70 до 80% пациентов достигли показателя EASI75 (т.е. улучшение не менее чем на 75% от состояния до лечения), а более 50 и 60% больных показали результат EASI90 в группах упадацитиниба 15 и 30 мг/сут. соответственно [18, 19]. Достигнутые результаты сохранялись и даже несколько увеличивались на протяжении 52 недель [20].
В ходе исследований помимо быстрого клинического ответа с первых дней лечения пациенты отмечали снижение интенсивности зуда [15, 19]. Высокая скорость действия упадацитиниба была также подтверждена в ином РКИ, Heads Up, при прямых сравнениях с дупилумабом, таргетным блокатором a-рецептора ИЛ-4 [21]. Джакиниб также продемонстрировал свою безопасность. Так, наиболее часто сообщаемыми побочными эффектами на фоне терапии оказались инфекции верхних дыхательных путей, обострения акне и АтД, головная боль и бессимптомное повышение уровня креатинфосфокиназы в крови, в большинстве случаев не требующими отмены препарата [15].
Заключение
Данный клинический случай демонстрирует превосходные результаты монотерапии упадацитинибом при рефрактерной к традиционным методам лечения форме АтД. Фармакологические особенности препарата обусловливают быстрый клинический эффект, удобство в использовании и отсутствие иммуногенности, т.е. сохранение ответа при повторных применениях. Возникший эпизод инфекции верхних дыхательных путей не стал причиной отмены лекарственного средства и не потребовал специфического лечения. Полученные результаты подтверждают эффективность и безопасность препарата в терапии АтД среднетяжелого и тяжелого течения.



